Follow-up: Proposals to Rebuild U.S. Capacity Gaps
"The advanced capabilities are offshore. We push the buttons." - Industrial Policy # 12
The numbers don’t lie: from 2000 to 2022, the U.S. lost ground in every decile of export complexity, with China surging ahead—especially at the high end. Last issue, we saw how Belton and Zenick’s economic complexity framework maps this vulnerability. Now, we turn to the fix. This piece tackles the 10 most urgent capacity gaps they’ve identified—spanning industrial machinery to precision parts—and offers a playbook to close them. With targeted policies like subsidies and reshoring incentives, we can reverse the trend.
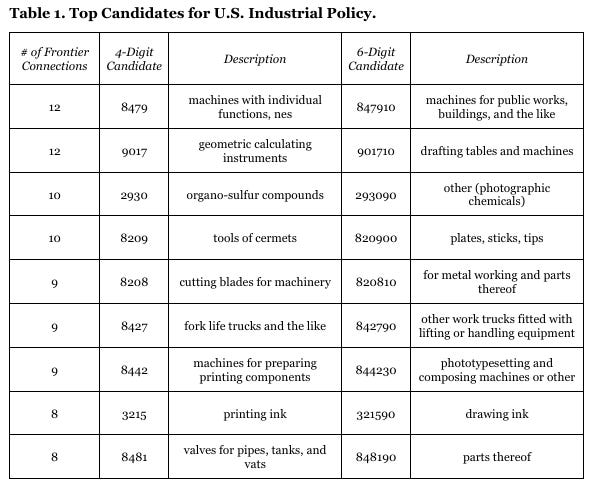
The 9 capacity gaps Belton & Zenick flag
I use slightly different descriptions below (with help from ChatGPT 5 and Grok). The 10th is the meta-capability: general purpose metal-cutting machine tools. 🤘
Let’s dive into the weeds...
Thank you for subscribing. This is public content. If you are not a member, please sign up here.
Proposals to Rebuild Capacity Gaps
1) Special-Purpose Industrial Machinery (HS 8479.10)
What it is
Non-standard machinery for public works, mining, and factory automation; often custom platforms integrating sensors, drives, and controls.
Why it matters
Seeds automation across fabs, EV/battery lines, and energy projects; co-export with a dozen frontier goods.
What blocks it
Lumpy demand; long payback on demo lines; vendor-qualification risk for primes.
12–36-month actions (Owner × Lever × Target)
DOC + DoD — Demand aggregation: 3-year framework contracts for standardized sub-platforms; include reference factory buys (10–15 lines).
Treasury/DOE — Targeted Section 48C (Advanced Energy Project) ITC: up to 30% credit (6% base / 30% with prevailing wage & apprenticeship) for domestic assembly and test cells tied to U.S. content in motion control.
NIST MEP — Vendor-qualification sprints: Fund 50 SME suppliers through OEM qual and ISO upgrades.
Risks & mitigations
Over-customization → require modular SKUs; export retaliation → prioritize non-substitutable niches.
Metrics (by Month 24)
10 domestic lines installed; median lead time to U.S. buyers ↓ 20%; import share in targeted SKUs ↓ 10 pts.
2) Precision Metrology & Alignment Instruments (HS 9017.10; adj. 9031)
What it is
Precision geometric instruments, optical profilers, interferometers, alignment systems used in aerospace and lithography.
Why it matters
Nanometer-scale accuracy underpins chipmaking, optics, and satellite/aero assemblies; metrology is the rate-limiter for yield ramp.
What blocks it
Thin domestic cluster; long standards/certification cycles; shortage of metrology engineers and optics/tooling talent.
12–36-month actions (Owner × Lever × Target)
NIST — Round-robin calibration program1: Subsidize inter-lab comparisons and national traceability; publish open qualification datasets.
USCIS/State — Fast-track visas: Dedicated O‑1/H‑1B lane for metrology/optics engineers; employer attestations via MEP.
DoD/NSF — SBIR/STTR2 set-aside: Alignment sensors and in‑situ metrology for advanced packaging; 50 Phase IIs with matching from primes.
State/MEP — Cluster grants: Support two metrology hubs co-located with optics and precision machining shops.
Risks & mitigations
Fragmented demand → create pooled buying via reference fabs; IP leakage → export-control aligned NDAs and onshore test.
Metrics (24–36 mo)
Lead times ↓ 25%; 200 new metrology roles filled; 100+ SKUs with NIST-traceable certificates made in U.S.
3) Organo‑Sulfur Specialty Chemicals (HS 2930.90)
What it is
Specialty organo-sulfur intermediates for photoresists, EV battery additives, and pharma.
Why it matters
Feedstocks for semiconductors, clean energy, and critical drugs; chokepoint chemicals can idle billion-dollar lines.
What blocks it
Site permitting, waste treatment, hazmat logistics; off‑take uncertainty; need for rail/steam/utilities co-location.
12–36-month actions (Owner × Lever × Target)
DOE LPO — Project guarantees: Support on‑site waste‑treatment and utilities at two chemical parks; require domestic offtake.
GSA/DoD/DOE — Long-term offtakes: 5–7‑year contracts for defined intermediates (photoresist/battery grades).
EPA — Green-chemistry grants: Process intensification & solvent recovery; expedite permits for low-emission designs.
States — Industrial sites: Pre‑permitted parcels with rail/steam; tax increment for onsite treatment CAPEX.
Risks & mitigations
Community opposition → transparent monitoring and escrowed remediation funds; demand risk → multi-agency offtake pool.
Metrics (36 mo)
Domestic capacity +30 kt/yr in target SKUs; >60% U.S.‑sourced binders/solvents for selected photoresists; incident rate below industry benchmarks.
4) Cermet Cutting Inserts & Tips (HS 8209.00)
What it is
Cermet inserts for high-speed machining of nickel superalloys and titanium.
Why it matters
Drives precision and tool life in aerospace/energy parts; uptime and edge retention set cell economics.
What blocks it
Cobalt/nickel powder supply; sintering furnace lead times; know‑how concentrated abroad.
12–36-month actions (Owner × Lever × Target)
Treasury — 100% bonus depreciation: For domestic powder‑metallurgy lines and sintering furnaces meeting yield KPIs.
Congress/Treasury — 45X‑style production credit: Per‑kg credit for cermet powder made in U.S.
DARPA/DOE — Materials program: Cold‑spray/coatings to extend tool life; public testbeds with OEMs.
Risks & mitigations
Powder pricing volatility → indexed offtake; environmental → closed-loop powder recovery standards.
Metrics (24–36 mo)
Tool life +25%; domestic share of aerospace‑grade inserts +15 pts; two new sintering lines commissioned.
5) Carbide & HSS Machine Blades (HS 8208.10)
What it is
Precision blades/knives for milling, slitting, and grinding; core to medical, optics, and packaging lines.
Why it matters
Tolerance stack drives yield in med‑device and optics; downtime costs cascade across production cells.
What blocks it
Aging grinder base, metrology gaps, and a shortage of skilled grinder/operators.
12–36-month actions (Owner × Lever × Target)
NIST MEP + States — Modernization vouchers: $250k–$1M per shop for in‑line metrology, adaptive controls, and coolant systems.
Treasury — Temporary 100% bonus depreciation: For grinder retrofits meeting energy/yield KPIs (mirrors 179D logic).
Community Colleges + OEMs — Grinder academies: 12‑month paid programs with OEM-provided machines; 500 graduates/year.
Risks & mitigations
Quality drift → vouchers tied to SPC adoption and external calibration audits.
Metrics (24–36 mo)
Scrap rates ↓ 25%; domestic output +20%; 300+ new certified grinder techs/year.
6) Forklifts & Material‑Handling Equipment (HS 8427.90)
What it is
Lift trucks, AGVs, batteries, and safety subsystems used in every fab, warehouse, and shipyard.
Why it matters
It’s the transport/logistics layer; delays ripple through construction and fab ramp.
What blocks it
Thin final‑assembly footprint, local battery packs, and safety‑certified electronics BOMs.
12–36-month actions (Owner × Lever × Target)
GSA + USPS + DoD — Federal fleet pull‑through: Commit to U.S.-assembled lift trucks; publish a 3‑year demand schedule.
DOE LPO + IRA domestic‑content adders: Tie battery subsidies to U.S. pack assembly for MHE; supply‑chain guarantees for motors/controllers.
OSHA + NIST — Raise standards, don’t “preference”: Update safety rules to require advanced sensing/telematics; fund U.S. vendors to certify.
Risks & mitigations
Price delta vs imports → TCO pilots (charger/network + uptime); workforce → OEM‑run technician training.
Metrics (24 mo)
30% of federal MHE purchases U.S.-assembled; 2 new pack plants qualified; downtime/incident rates ↓ 15%.
7) Roll‑to‑Roll Patterning & Registration (HS 8442.30; adj. 8443)
What it is
Pre‑press/phototypesetting lineage tools for flexible electronics and security printing—high-precision web handling, patterning, and registration.
Why it matters
Enables flexible displays, printed sensors, security features; a bridge between lab recipes and scaled production.
What blocks it
Gaps in pilot‑line access; fragmented IP across web handling, inks, and curing; few domestic OEMs.
12–36-month actions (Owner × Lever × Target)
NSF Manufacturing USA — New node: Shared pilot coat/dry/inspect lines with cleanroom access; 100 SME runs/year.
DoD/Treasury — Tooling ITC: 20% credit for precision web-handling platforms meeting registration specs.
SBA — SBIR set‑aside: Retrofitting legacy printers for functional layers; 40 Phase IIs.
Risks & mitigations
Under‑utilization → anchor tenants (defense/security printing); IP friction → standardized test licenses.
Metrics (36 mo)
50 qualified process “recipes”; uptime ≥ 85%; 10 U.S. OEM platforms in production.
8) High‑Performance Printing Inks (HS 3215.90; adj. pigments 3206; resins 3909/3911)
What it is
Functional inks for sensors and additive electronics; depends on specialty pigments/resins.
Why it matters
Critical to wearables, IoT, and printed electronics; supply determines device yield and reliability.
What blocks it
Pilot‑scale bottlenecks; dependence on imported pigments/resins; EHS compliance costs.
12–36-month actions (Owner × Lever × Target)
UK‑Catapult‑style pilot lines (DOC/NSF): Shared mixing/dispersion/print test lines; fee-for-service for SMEs.
Grant priority — Domestic inputs: Scoring boost for plants using U.S. pigments/resins; small grants to reshore key pigments.
Defense/NIH — Targeted offtake: Flexible sensors for training gear and medical wearables; multi‑year buys.
Risks & mitigations
Spec drift across batches → lot certification & digital batch passports; environmental → solvent recovery incentives.
Metrics (24–36 mo)
25 new U.S. ink SKUs qualified; domestic input share >50% for pilot lines; yield variance ↓ 30%.
9) Industrial Valves & Precision Parts (HS 8481.90; adj. forgings 7325/7326; seals 4016)
What it is
Valves and precision components for hydrogen, CCUS, LNG, and semi fabs.
Why it matters
Capex schedule keeper for energy/semiconductor projects; certification gates project risk.
What blocks it
ASME/API certification backlog; forging/casting and elastomer bottlenecks; working‑capital strain for long-cycle orders.
12–36-month actions (Owner × Lever × Target)
ASME/API + DOE — Accelerated cert program: Funded test capacity and fast‑track audits for U.S. shops.
DOE LPO — Buy America clauses: Tie LPO loan guarantees to U.S.-made valves/parts where feasible.
NIST MEP — Die‑shop vouchers: Modernize forging/casting die makers and QA; supplier development for elastomer seals.
Risks & mitigations
Cost spikes → multi‑year pricing with escalation clauses; QC risk → third‑party inspection pools.
Metrics (24–36 mo)
Lead times ↓ 20%; 500 additional certified SKUs; domestic share in DOE‑backed projects +15 pts.
10) General‑Purpose Metal‑Cutting Machine Tools (HS 8457.10/.30; adj. 8456/8459/8460)
What it is
Five‑axis machining centers, EDM/laser, precision grinders—the meta‑capability that makes other tools.
Why it matters
Governs ~30% of frontier goods; concentrates know‑how in fixtures, metrology, motion control.
What blocks it
Export‑finance gap vs peers; demo‑line CAPEX; fragmented SME demand; thin grinder/toolmaker pipeline.
12–36-month actions (Owner × Lever × Target)
Ex‑Im + DFC — Export scale window: Facility for machine‑tool OEMs; blended finance for overseas buyers of U.S. five‑axis/EDM.
Treasury/DOE — Targeted 48C: ITC for ultra‑precision platforms tied to kWh/part efficiency.
DoD/DOC — Reference factories: Two lines each for aerospace/medical demo parts with multi‑year parts orders.
MEP + Colleges — Tool/grind academies: Paid residencies; 500 graduates/yr by Year 3; fast‑track visas for master grinders.
Risks & mitigations
Commodity creep → restrict to ultra‑precision niches; energy draw → efficiency‑linked credits.
Metrics (36 mo)
10 new domestic lines; 20% shorter lead times; U.S. share of domestic five‑axis purchases +10–15 pts.
If you read this far, thank you—we clearly have a shared interest. Please consider hitting the like button, it helps others discover us, or consider subscribing to a paid tier to support my work. Comments are only open to premium members, but feel free to DM me with any thoughts.
“Ring trial” where a reference artifact (piece) gets passed around labs, each lab measures it and records results, then NIST organizer analyzes the data and issues a report to get the labs to tighter up their methods and improve NIST traceability.
SBIR/STTR are the U.S. government’s main non-dilutive R&D programs for small businesses:
SBIR = Small Business Innovation Research.
Agencies reserve (“set aside”) a small % of their extramural R&D budgets to fund startups/SMBs to prove feasibility (Phase I) and build prototypes (Phase II). Phase III is commercialization—often via government procurement—without SBIR funds.STTR = Small Business Technology Transfer.
Similar money, but requires a formal research-institution partner (university, FFRDC). Typical workshare: small biz ≥40%, research partner ≥30% (rest flexible). It’s designed to pull lab IP into products.